Structure- and Property-Based Design of Factor Xa Inhibitors: Pyrrolidin-2-Ones with Acyclic Alanyl Amides as P4 Motifs.
Young, R.J., Campbell, M., Borthwick, A.D., Brown, D., Burns-Kurtis, C.L., Chan, C., Convery, M.A., Crowe, M.C., Dayal, S., Diallo, H., Kelly, H.A., Paul King, N., Kleanthous, S., Mason, A.M., Mordaunt, J.E., Patel, C., Pateman, A.J., Senger, S., Shah, G.P., Smith, P.W., Watson, N.S., Weston, H.E., Zhou, P.(2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 5953
- PubMed: 16982190
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.09.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2J4I - PubMed Abstract:
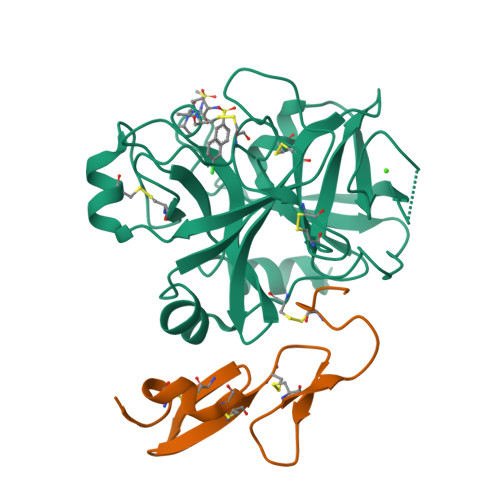
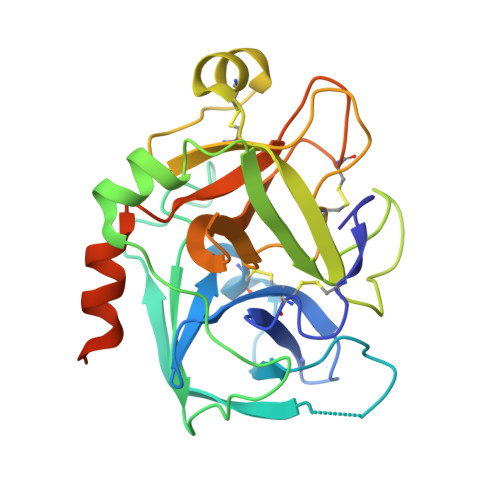
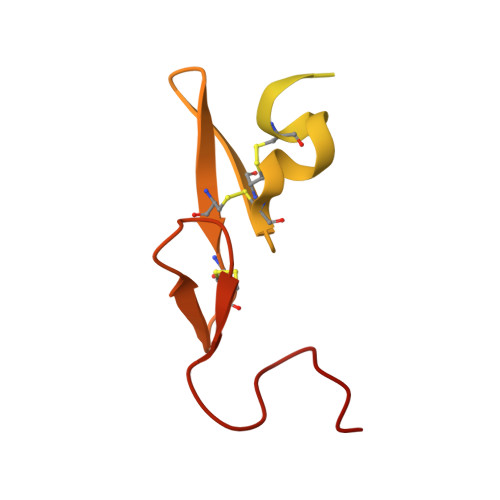
Structure-based drug design was exploited in the synthesis of 3-(6-chloronaphth-2-ylsulfonyl)aminopyrrolidin-2-one-based factor Xa (fXa) inhibitors, incorporating an alanylamide P4 group with acyclic tertiary amide termini. Optimized hydrophobic contacts of one amide substituent in P4 were complemented by hydrophobicity-modulating features in the second, producing potent fXa inhibitors including examples with excellent anticoagulant properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
GlaxoSmithKline, Medicines Research Centre, Gunnels Wood Road, Stevenage, Hertfordshire SG1 2NY, UK. Rob.J.Young@gsk.com